Definition of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are the compounds which carry electric charge and present in the body fluids, tissues and cells.
Body fluids contain various organic and inorganic compounds. The concentration of these compounds in body is balanced in such a way that body cells and tissues are having same environment. To maintain this balance, body has various regulatory mechanisms like osmotic balance, pH and ionic balance which help to keep constant solute concentration in body fluids.
Importance of Electrolytes in body:
It is essential to maintain the electrolyte concentration in our body for normal functioning of cells and tissues, muscle coordination, heart function, fluid absorption and excretion, and nerve function.
If person undergoes surgery or remain ill for long period, body can not maintain the electrolyte concentration and that time it’s necessary to supply electrolytes externally to body. This therapy is called as replacement therapy. In this therapy, various electrolytes, carbohydrates, protein, amino acids and blood products are provided to patient as per their need.
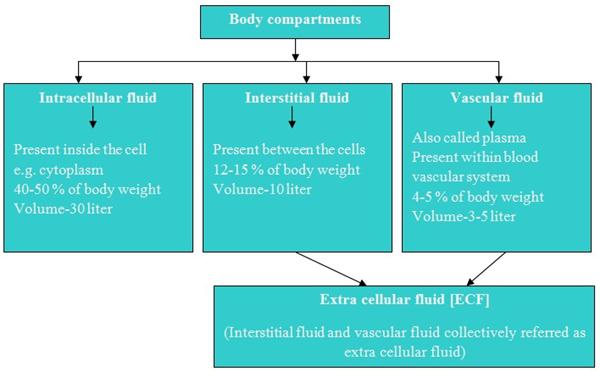
The concentration of various electrolytes in body compartments is different and shown in table.
| Inorganic ions |
Extra cellulars electrolytes
mEq/L |
Intracellular electrolytes
mEq/L |
Plasma
mEq/L |
Cations
Sodium
Potassium
Calcium
Magnesium |
142
4
2.4
1.2 |
10
140
0.0001
58 |
135-145
4.5-5.5
2.1-2.6
1.5-3.0 |
Anions
Chloride
Sulphate
Bicarbonate
Phosphate |
103
1
28
4 |
4
2
10
75 |
98-105
0.3-1.5
25-31
1.2-3.0 |
Function of Electrolytes in body;
To maintain acid-base balance in body
To control osmosis of water between body compartments
For transmission of nerve impulses
For contraction of muscles
For secretion of hormones and neurotransmitters
To generate action potential and graded potentials