Plant Biology - Leaf morphology
Leaf morphology:
A flat, green and extensive lateral adjunct developed form the node of the stem or its branches is called leaf.
Section of leaf:
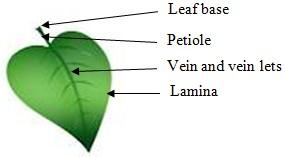
1. Leaf base – part of leaf which is attached to the node of the stem and sometimes contains a pair of lateral outgrowths (Stipules) which are small and look like leaf only.
2. Petiole – A middle part of the leaf which connects leaf base and lamina. It is a stalk like structure and arranges the lamina to get proper sun light.
Petiole is present in a leaf – Petiolate leaf
Petiole is absent in a leaf – Sessile leaf
3. Lamina – Main part of the leaf which is broad, green and flat. It contains veins and vein lets. The arrangement of veins and vein lets in leaf is called venation and is of two types either reticulate or parallel. Vein transfers water, food and essential minerals in the lamina and forms skeletal network within it.
Types of leaf:
1. Simple leaf:
Leaf containing single lamina and auxiliary bud at its axis is called simple leaf. Lamina appears dissected from the margin however notch is incomplete.
2. Compound leaf:
Lamina is divided into independent leaflets and notch is completed and reaches to the tip of the petiole is called compound leaf. It does not contain auxiliary bud.
a) Pinnate: leaf lets are arranged on both lateral sides of the main vein
Unipinnate – Leaflet is present on the main midrib e. g. cassia
Bipinnate – Leaflets are present on the secondary branches e.g. Acacia
Multipinnate – Many leaflets are presents on the higher order branches e.g. Moringa
b) Palmate: leaf lets are arranged on the tip of the petiole.
Unifoliate – Single leaf let at the tip of the petiole e.g. lemon
Bifoliate – Two leaves let on the tip of the petiole e.g. Balanites
Multifoliate – Many leaves lets on the tip of the petiole e. g. Bombax
Phyllotaxy:
The arrangement of leaves on stem or its branches are called Phyllotaxy.
1. Alternate Phyllotaxy – single leaf arises from a node on stem e.b. sunflower
2. Opposite Phyllotaxy – two leaves arises from a single node opposite to each other.
Opposite decussate – Leaves are arranged at right angle to each other e. g. Catotropis
Opposite superimposed – Leaves are arranged by over lapping one another e. g. Guava
Whorled – more than two leaves are arranged at each node e. g. Red oleander
Function of Leaf:
1. By photosynthesis, it prepares food require for plant growth.
2. Helps in respiration
3. Helps in transpiration process by loosing water in form of water vapor
4. Stores food in special cases e. g. onion
5. Helps in support and climbing e.g. Gloriosa, Smilax
6. Helps in protection by transforming into a sharp pointed structure called spine e.g. acacia, agave
7. Leaf are modified into pitcher or a bladder in capturing insects e. g. Nepenthes, Utricularia
Self study:
Q-1: A small lateral outgrowth present at the leaf base is called ………………
a) Stipule
b) Vein
c) Petiole
d) Leaf apex
Answer: A small lateral outgrowth present at the leaf base is called stipule
Q-2: Venation is the arrangement of ……………..and ……… in lamina of the leaf
a) Leaf and leaf lets
b) Pinnate and palmate
c) Vein and vein let
d) None of above
Answer: Venation is the arrangement of vein and vein let in lamina of the leaf
Q-3: Match the following
| A |
B |
| Pinnate leaf |
Single lamina with auxiliary bud |
| Palmate leaf |
Arrangement of leaves on stem or its branches |
| Single leaf |
Leaflets are arranged on the tip of the petiole |
| Phyllotaxy |
Leaf lets are arranged on both the sides of the midrib |
Answer:
| A |
B |
| Pinnate leaf |
Leaf lets are arranged on both the sides of the midrib |
| Palmate leaf |
Leaflets are arranged on the tip of the petiole |
| Single leaf |
Single lamina with auxiliary bud |
| Phyllotaxy |
Arrangement of leaves on stem or its branches |