Properties of the Identity Matrix
A matrix multiplied by its inverse is equal to the identity matrix.
A · A-1 = A-1 · A = I
All the elements of the matrix apart from the diagonal are zero.
For an m × n matrix A:
Im A = A In = A
Example 1: If 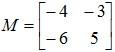 , then find M × I, where I is an identity matrix.
, then find M × I, where I is an identity matrix.
Solution:
As M is square matrix of order 2×2, the identity matrix I needs to be of the same order 2×2. [Rule for Matrix Multiplication.]
Thus:
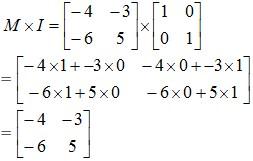
Example 2: Determine the value of x, y and z if:
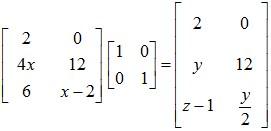
Solution:
On the L.H.S we have:
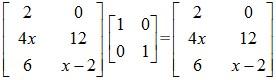
Now, we compare the L.H.S matrix with the R.H.S matrix in order to determine the values of x, y and z.
y = 4x ……….(1)
z – 1 = 6 ……(2)
x – 2 = y/2 ……(3)
From (2) we can determine the value of z, which is z = 7.
From (3) we can simplify the equation to y = 2x – 4
We now have two equations with two unknown factors, namely x and y:
y = 2x – 4
y = 4x
To determine the value of x and y, simply insert y = 4x into y = 2x – 4, which will give us:
4x = 2x – 4 => x = – 2
And y = 4x = – 8
Hence (x, y, z) = (-2, -8, 7)