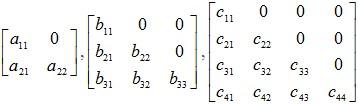Triangular matrices: A square matrix with elements sij = 0 for j < i is termed upper triangular matrix. In other words, a square matrix is upper triangular if all its entries below the main diagonal are zero.
Example of a 2 × 2 upper triangular matrix:
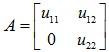
A square matrix with elements sij = 0 for j > i is termed lower triangular matrix. In other words, a square matrix is lower triangular if all its entries above the main diagonal are zero.
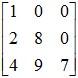
Example of a 3 × 3 lower triangular matrix:
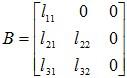
· Diagonal matrices are both upper and lower triangular since they have zeroes above and below the main diagonal.
· The inverse of a lower triangular matrix is also lower triangular.
· The product of two or more lower triangular matrices is also lower triangular.
· The transpose of a lower triangular matrix is upper triangular.
· The inverse of an upper triangular matrix is also upper triangular.
· The product of two or more upper triangular matrices is also upper triangular.
· The transpose of an upper triangular matrix is lower triangular.
Example 1: Classify the following matrices into upper and lower triangular matrices:

Solution:
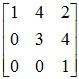 : Upper Triangular Matrix
: Upper Triangular Matrix
 : Lower Triangular Matrix
: Lower Triangular Matrix
 : Lower as well as Upper Triangular Matrix
: Lower as well as Upper Triangular Matrix
 : Upper Triangular Matrix.
: Upper Triangular Matrix.
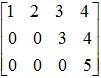 : Neither Upper nor Lower Triangular Matrix because it is not a Square Matrix.
: Neither Upper nor Lower Triangular Matrix because it is not a Square Matrix.
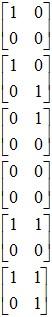
Example 2: Using only elements 0 and 1’s, find all 2 × 2 upper triangular matrices.
Solution: Upper triangular matrices must have 0’s below the diagonal. This gives the following matrices.
Example 3: Exhibit the generic lower triangular matrices of order 2, 3 and 4.
Solution: Generic lower triangular matrices of order 2, 3 and 4 can be given as follows: